If you connect to the Internet, allowing others to use your computer, or share files with others, you should take steps to protect your computer against the damage. Why? Because there are computer criminals (sometimes called hackers or crackers) who attack other people's computers. These people can attack, breaking into your computer via the Internet and stealing your personal information, or indirectly, by creating malicious software (or malware) to damage your computer.
Fortunately, you can protect yourself by taking some simple precautions. This article describes the threats and what you can do to defend against them.
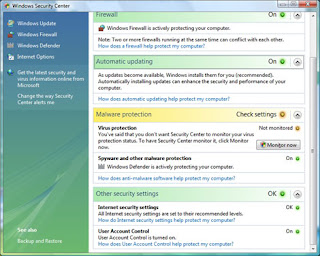
Check your security status with Windows Security Center
Windows Security Center is your headquarters for computer security. It shows your current computer and the security recommends something you need to do to help make your computer more secure. To open:
Click here to open Security Center.
The safety checks your computer for these essential security elements:
Firewall. A firewall can help protect your computer by preventing hackers or malicious software to access it.
Automatic update. Windows can check regularly for updates for your computer and install them automatically.
Malware protection. Antivirus software can help protect your computer against viruses, worms and other threats to security. Antispyware software can help protect your computer against spyware and other unwanted software.
Other security settings. The safety profile for a good Internet security settings and User Account Control is enabled.
If any of the security elements have a red or yellow, your computer may be vulnerable to security threats. To solve the problem, click an item to expand it, then follow the instructions.
What are security alerts?
If Windows detects that your computer may need to strengthen security in a security area-firewall, automatic updates, malware protection, or other security settings, you will see a notification each When you connect until the problem is resolved. The notifications are displayed in the notification area of the taskbar.
Click on the notification to open Security Center, where you can learn how to solve the problem.
Note
To disable notifications of security or hide the safety icon in the notification area, open security, click Change the way Security Center alerts me, and then choose an option. Even if you disable notifications, security will continue to verify and display the state of security.
Use a firewall
A firewall hardware or software that checks the information from the Internet or a network and then it turns immediately or it can pass through your computer, depending on your firewall settings. In this way, a firewall helps prevent hackers and malware from accessing your computer.
Windows Firewall is integrated with Windows and is automatically activated.
If you run a program as an instant messaging program or network multiplayer game that should receive information from the Internet or a network, the firewall asks if you want to block or unblock (allow) the connection. If you choose to unblock the connection, Windows Firewall creates an exception so that the firewall will not bother you at this issue needs to receive information in the future.
Use protection against viruses
Viruses, worms and Trojan horses are programs created by hackers who use the Internet to infect vulnerable computers. Viruses and worms can replicate from computer to computer, while the Trojans enter a computer by hiding in a seemingly legitimate program as a screen saver. Destructive viruses, worms, Trojan horses and can delete information from your hard disk or completely disable your computer. Others do not cause direct damage, but worsen your computer's performance and stability.
Antivirus scan e-mail and other files on your computer from viruses, worms and Trojan horses. If there is, the virus is in quarantine (isolate), he or she removes all the damage before it your computer and files.
Windows does not have a built-in antivirus, but the manufacturer of your computer may have installed. Security check whether your computer has antivirus protection. If not, go to anti-Microsoft Partners Web page to find viruses.
Because new viruses are identified each day, it is important to choose an antivirus program with a capacity of patches. When the antivirus software is updated, it adds new viruses to its list of viruses to check, helping to protect your computer against new attacks. If the virus does not update, your computer is vulnerable to new threats. Updates usually require an annual subscription. Keep an existing subscription to receive regular updates.
Warning
If you do not use antivirus software, you expose your computer to damage from malicious software. You can also run the risk of spreading viruses to other computers.
Use spyware protection
Spyware is software that can display advertisements, collect information about you or change the settings on your computer, generally without appropriately obtaining your consent. For example, spyware can install unwanted toolbars, links or bookmarks in your Web browser, change your default home page, display or pop-up often. Some spyware do not have symptoms displays that you can detect, but secretly collect sensitive information, such as Web sites you visit or the text that you type. Most spyware is installed by free software you download, but in some cases, simply visiting a Web site results from infection with spyware.
To help protect your computer against spyware, use an antispyware program. This version of Windows has a built-in antispyware called Windows Defender, which is enabled by default. Windows Defender notifies you when spyware tries to install it on your computer. It can also scan your computer for spyware and then delete it.
Because new spyware appears every day, Windows Defender must be updated regularly to detect and protect against the latest spyware threats. Windows Defender is updated every time you update Windows. For the highest level of protection, set Windows to install updates automatically (see below).
Windows update automatically
Microsoft regularly offers important updates for Windows that can help protect your computer against new viruses and other threats to security. To ensure you receive these updates as quickly as possible, turn on automatic updating. In this way, you do not have to worry that critical fixes for Windows might be missing from your computer.
Updates are downloaded in the background when you are connected to the Internet. Updates are installed à 3h00 unless you specify another time. If you turn off your computer before then, you can install the updates before shutting down. Otherwise, Windows will install the next time you start your computer.
To activate the automatic update
Click to open Windows Update.
Click on Edit Settings.
Make sure you install updates automatically (recommended) is selected. Windows will install important updates for your computer as they become available. Important updates provide significant benefits such as improved security and reliability.
Under recommended updates, make sure Include recommended updates when downloading, installing, or notifying me about updates check box is selected, then click OK. Recommended Updates are non-critical problems and help improve your computing experience. If you are prompted to enter an administrator password or confirmation, type the password or provide confirmation.
Use a standard user account
When you connect to your computer, Windows grants you a certain level of rights and privileges depending on the type of user account that you have. There are three types of user accounts: standard, administrator, and customers.
Even if an administrator account provides complete control over a computer, using an account can help make your computer more secure. That way, if other people (or hackers) access your computer while you are connected, they can not touch the computer's security settings or modify other user accounts.
To determine your type of account
Click to view user accounts.
The type of account is under your name.
If you are currently using an administrator account, see Changing a user account type to learn how to change a standard.
Tips for using e-mail and Web Security
Be cautious when opening e-mail attachments. e-mail attachments (files attached to e-mails) are the main source of infection by the virus. Never open an attachment from someone you do not know. If you know the sender but not expecting an attachment, verify that the sender actually sent the attachment before opening it. See When to trust an e-mail and avoid e-mail virus.
Protect your personal information carefully. If a Web site requires a credit card number, bank account information or other personal information, make sure you trust the Web site and verify that its transaction system is secure. See When to trust a Web site.
Use anti-phishing filter in Internet Explorer. Phishing is the practice of creating fraudulent e-mails and Web sites to trick computer users to reveal personal or financial information. The fraudulent e-mail or website appears to be a trusted source, such as a bank, credit card company, or reputations online. The Phishing Filter helps detect phishing websites to protect yourself against scams. See Phishing Filter: frequently asked questions.
Be careful when you click on links in e-mails. Hyperlinks (links that open websites when you click them) are often used as part of phishing and spyware scams, but they can also transmit viruses. Just click on links in emails that you trust.
The installation of add-ons Web site that you trust. Web browser add-ons, including ActiveX controls, web pages for things like displaying toolbars, stock tickers, video and animation. However, add-ons can also install spyware or other malicious software. If a site asks you to install an add-on, make sure you trust before doing so. If you install ActiveX controls? and Internet Explorer add-ons: frequently asked questions.
